What is ankle arthroscopy?
Ankle arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that involves small incisions (each roughly about 5 millimeters – small enough to close with a single stitch) and using a small camera to assess the inside the ankle joint. Specially designed surgical instruments can be used to address specific pathology within the ankle.
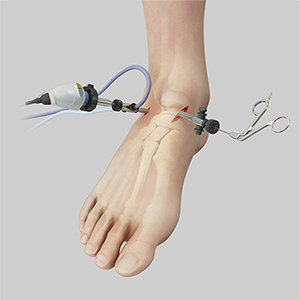 The instrument on the left is the arthroscope (camera) and the instrument on the right is a device called a grasper than can be used to clean up the ankle joint.
The instrument on the left is the arthroscope (camera) and the instrument on the right is a device called a grasper than can be used to clean up the ankle joint.
Which specific procedures can be performed arthroscopically?
There are numerous procedures that can be performed arthroscopically.
Some examples include:
- Debridement (cleaning up scar tissue and inflammatory tissue)
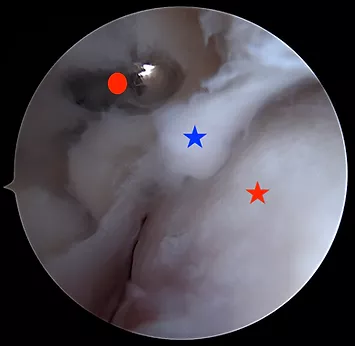
 This is a view of the inside of an ankle joint. The left side is the front of the ankle. The right side is the back of the ankle.
The red star is the talus bone (forms the bottom of the ankle joint).
The blue star is scar tissue in the joint.
The red circle is the shaver device.
This is a view of the inside of an ankle joint. The left side is the front of the ankle. The right side is the back of the ankle.
The red star is the talus bone (forms the bottom of the ankle joint).
The blue star is scar tissue in the joint.
The red circle is the shaver device.
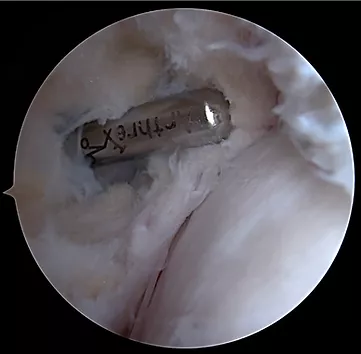
 This photo shows the shaver being used to clean up the scar tissue. Notice how the shaver has nicely removed the scar tissue.
This photo shows the shaver being used to clean up the scar tissue. Notice how the shaver has nicely removed the scar tissue.
- Removal of loose bodies (removing free pieces of bone and/or cartilage that are floating in the ankle joint)
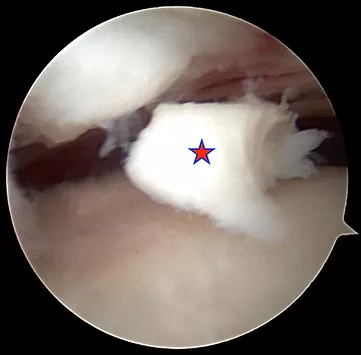
 The red star marks a loose body (free floating piece of cartilage) that was removed from an ankle joint.
The red star marks a loose body (free floating piece of cartilage) that was removed from an ankle joint.
- Treating cartilage injuries:
- If the damage is very minimal: the cartilage can be smoothed down
- If the damage is more substantial: a microfracture procedure can be performed (in which the cartilage is smoothed down and small holes are drilled into the underlying bone as so to allow bone marrow to flow out and encourage healing of the injured area
- Directly assessing for damage that are not clear based on x-ray’s
- There are multiple ligaments around the ankle and they can be directly visualized/assessed during ankle arthroscopy procedures
- Repair and reconstruction of ligaments: patients can have damaged ligaments are ligaments that are not functioning properly. These can be either repaired or reconstructed arthroscopically
- And much, much more!
What are the benefits of ankle arthroscopy?
There are numerous benefits, including:
- Ankle arthroscopy is safe and effective
- Surgery can be performed through very small incisions (lower rates of infection and wound healing problems)
- There can be less pain compared to more “open” surgeries that require larger incisions
- For certain situations, patients can start rehabilitation sooner
What are the possible downsides of ankle arthroscopy?
Some of the main risks of ankle arthroscopy include:
- Not all ankle issues can be treated arthroscopically. However, an arthroscopic procedure can easily be converted to a more “open” surgery if the goals of surgery cannot be achieved arthroscopically.
- Fluid extravasation: during ankle arthroscopy, fluid is used to fill the ankle joint to improve visualization. Sometimes, the fluid can seep into the surrounding tissues and cause swelling. This is generally temporary and resolves with time.
- Nerve irritation and injury: injuries to the nerves can happen and can manifest in the form of numbness or a burning sensation. Nerve injuries generally heal with time.
Is ankle arthroscopy right for me?
Dr. Anthony Yi would be happy to talk to you and discuss if an arthroscopic procedure is suitable for you!